RAW Denoise (Legacy)
For RAW images, instead of estimating the missing color information for each pixel based on the values of neighboring pixels, the AI model uses context from the entire image. It also considers and compensates for noise that hinders traditional demosaicing methods and fixes hot pixels.
When will RAW Denoise kick in?
The RAW Denoise model will kick in when when the program detects a RAW file show on a camera that has a Bayer sensor (Canon, Nikon cameras for example). If your camera is for example, a Fujifilm camera, it will have a X Trans sensor, and will not have this overall aggressive RAW noise that Bayer sensor camera have. RAW Denoise is not needed for X trans sensors. For any noise on these X Trans files, you can use the regular Denoise enhancement (it would be to remove the low-light noise and not RAW noise)
Controls
Use the Controls tab to select the AI model and adjust the settings.
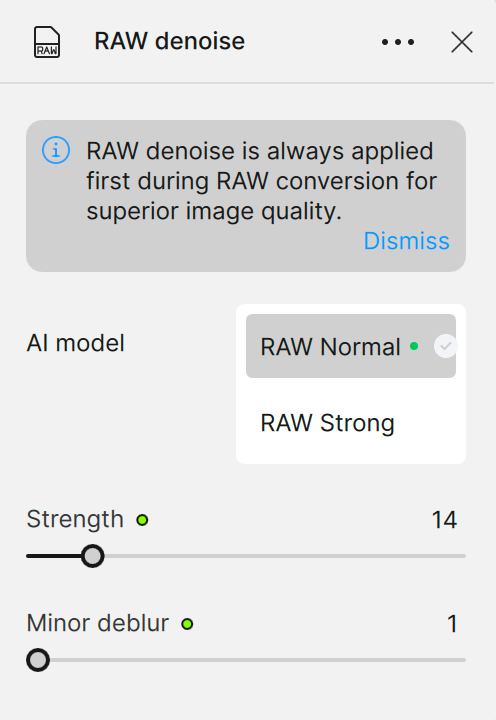
AI Models
RAW Normal
Use the RAW Normal model to treat the vast majority of RAW images since most cameras have built-in noise reduction.
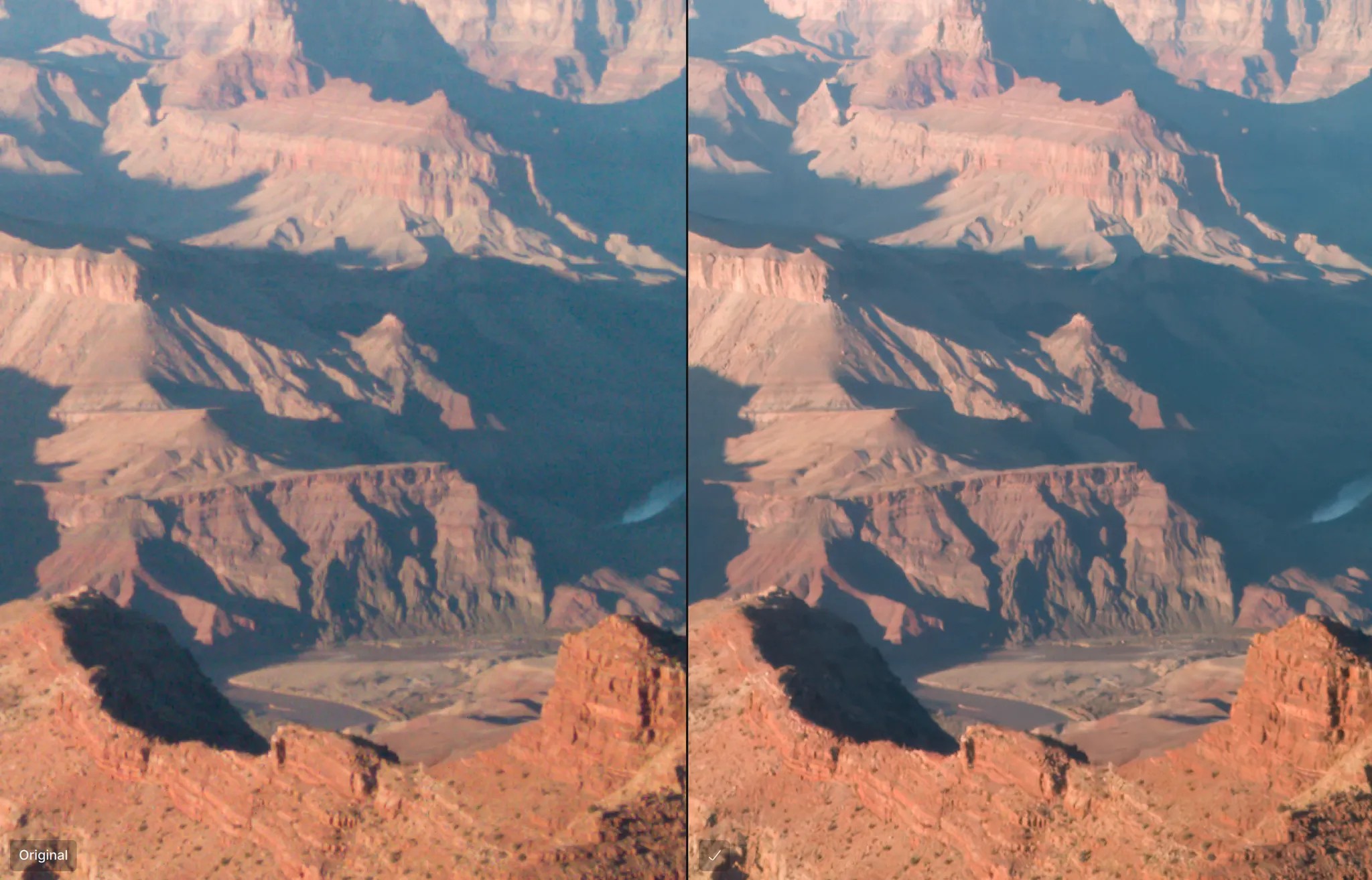

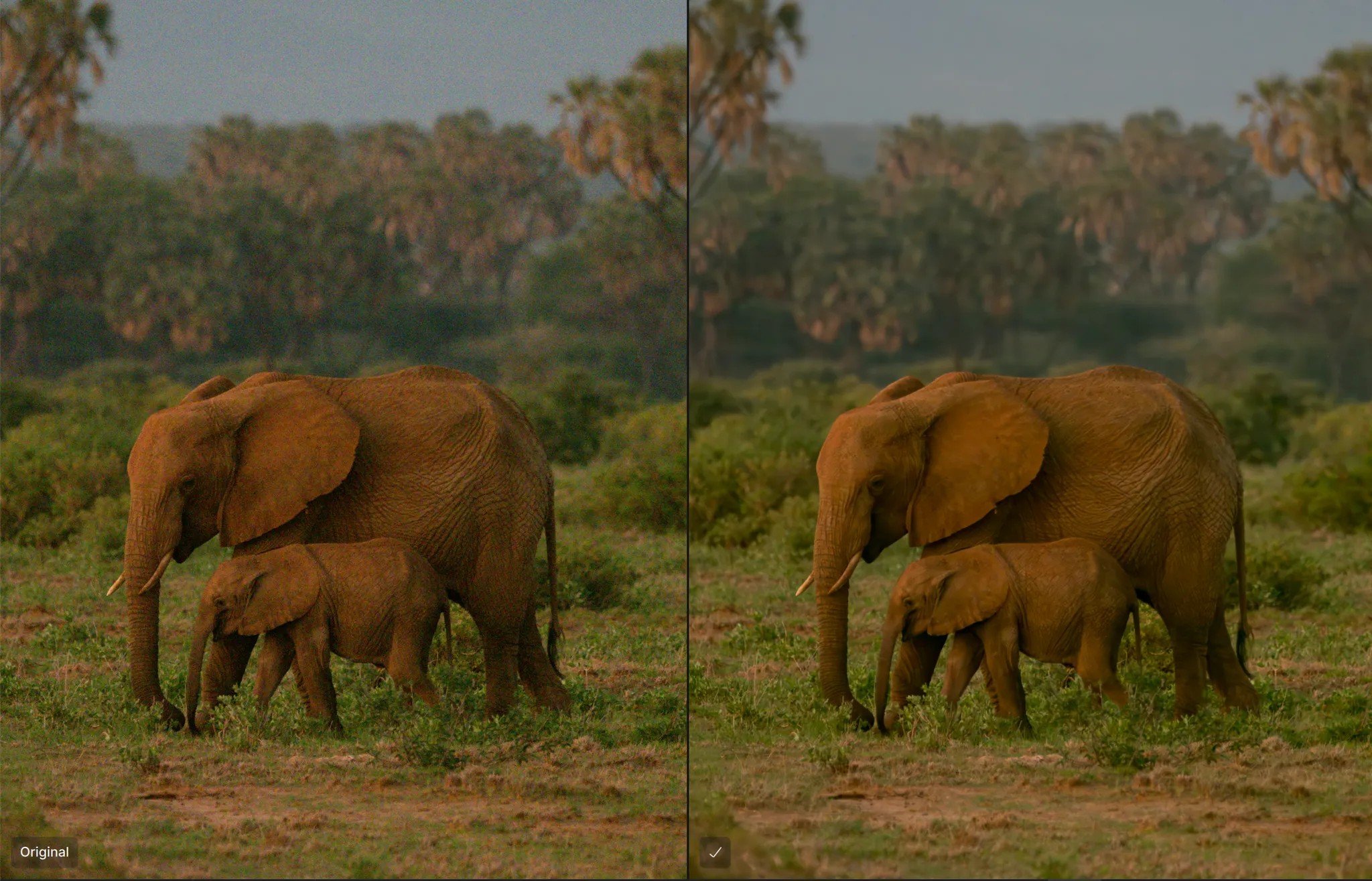
RAW Strong
This model is reserved for severe noise due to very high ISO (above 6400 ISO). Use it to recover details in images shot in low light.

Preferences
Open the Photo AI Main Menu > Preferences > RAW denoise
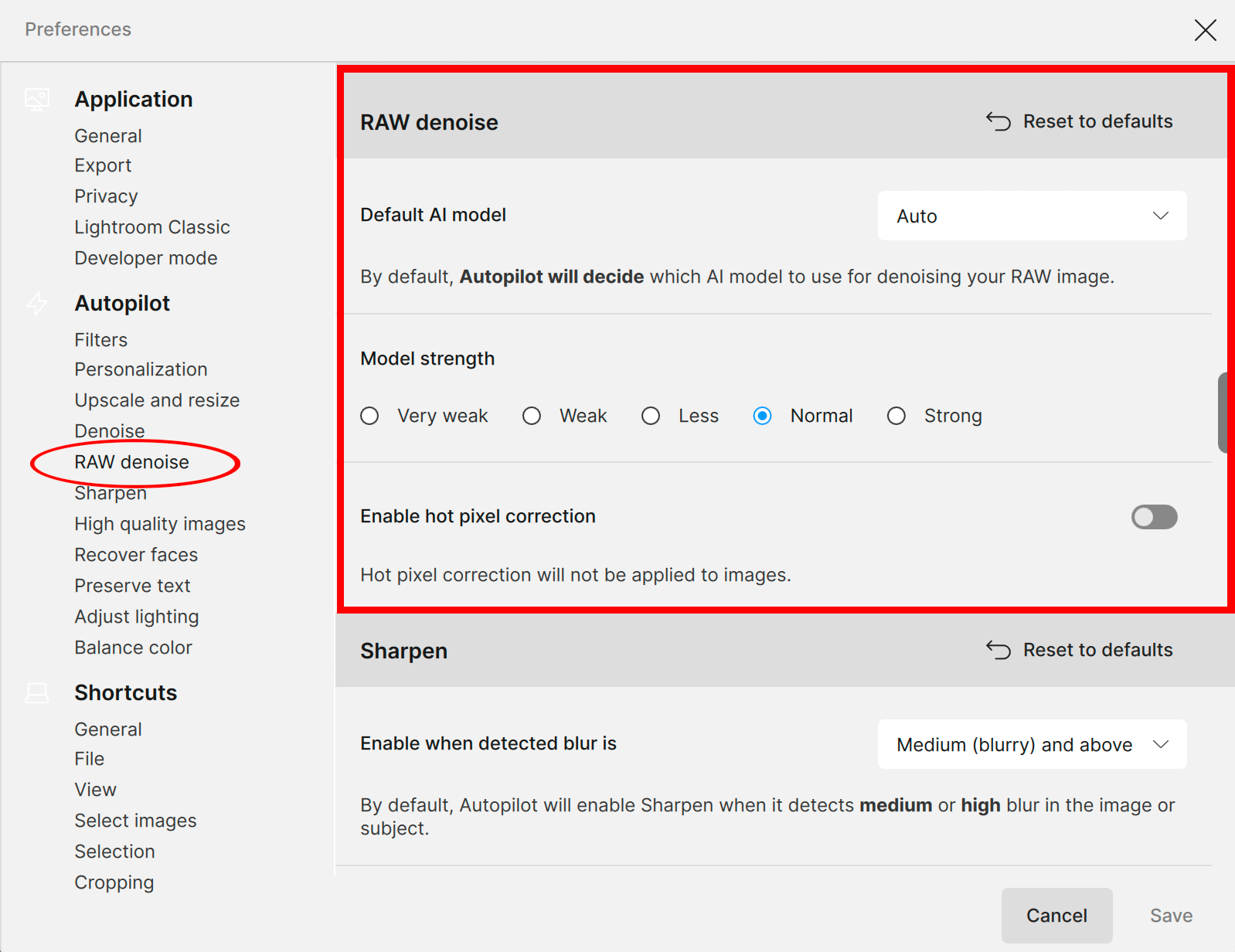
- Default AI Model - select from the dropdown menu to choose between AUTO, RAW Normal, or RAW Strong as your go-to setting
- Model strength - adjust the model strength slider to a default setting
- Enable hot pixel correction - use this toggle to correct hot pixel issues. A hot pixel is a pixel that doesn't react to light or reacts in an unusual way, appearing as a bright dot in an image. Hot pixels can be caused by sensor age, contamination during sensor production, long exposure times, high gain settings, high sensor operating temperature, or manufacturing defects.