Images
The maximum upscale potential is a resolution of 32,000 pixels on the longest edge, or a file size of 2 GB; whichever comes first.
Gigapixel supports importing and exporting common image formats.
We recommend using a standardized RGB color space with a common color profile such as sRGB, Adobe RGB, or ProPhoto.
Formats
- JPG, JPEG
- PNG
- TIF, TIFF
- DNG
- RAW (We do not recommend using RAW images)
- JPEG
- PNG
- TIFF
Choosing Preserve input format will ensure that your JPG or TIF extension is maintained on export.
The following formats will import, but may show color inconsistencies depending on profile and bit depths:
- HEIF, HEIC
- WEBP
- PPM, PGM, PBM, PNM
We recommend processing RAW images in apps like Topaz Photo, Lightroom, Adobe Camera Raw, or Capture One and exporting as TIFF for use in Gigapixel.
Imported DNG & RAW files will be exported as TIFF if Preserve input format is selected in the Export dialog.
Support for CMYK output is only compatible as a TIFF export.
Resolve Issues
If your image fails to import or export, confirm that its format (encoder/wrapper), and colorspace are in the supported list above.
If you see strange color shifts in the preview, the color space or color profile of your image may not be directly supported and should be converted before importing. Your display settings can also create undesired color shifts.
If you're attempting to import an image that is already very large, you may not see the 4x or 6x scale factors in the Upscale section. This is because upscaling with those factors would exceed the maximum pixel dimension of 32,000px.
If your image appears black/blank in the preview, you either have an unsupported image or the filename includes a "?" that needs to be removed. Ensure that folder names and file titles do not include any question marks.
Cloud sync file paths are not supported. Move files to out of Dropbox, Google Drive, One Drive, and iCloud Drive folders before importing to Gigapixel.
Plugins
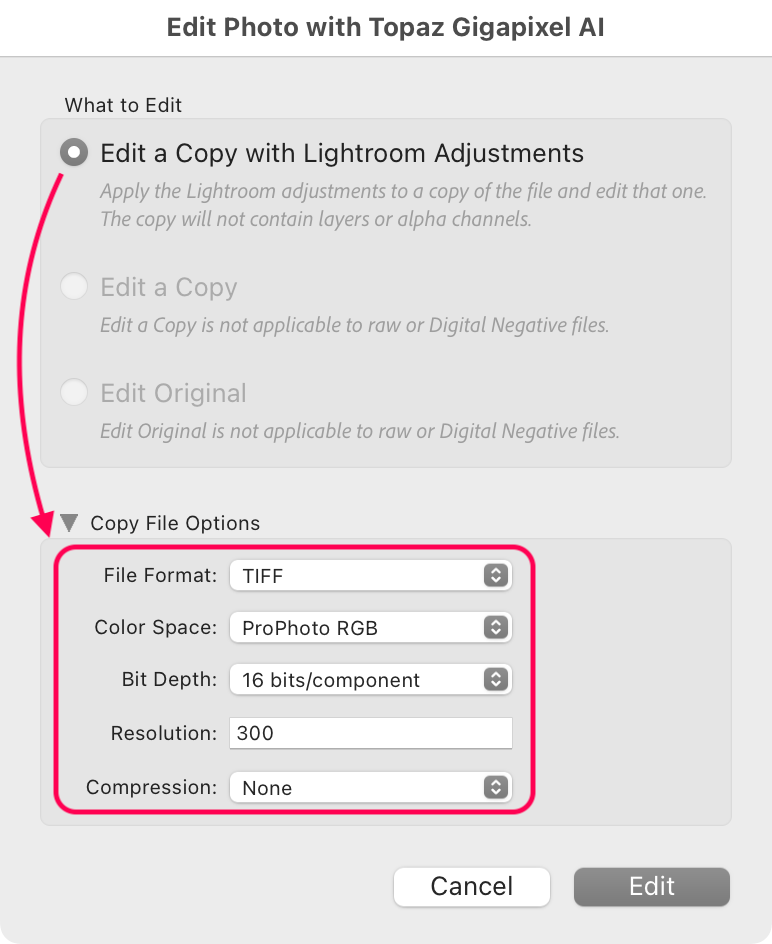
Depending on the image source, we recommend choosing the option to "Edit a Copy," with or without adjustments. The format you choose in the File Format menu will be the format that Gigapixel exports and returns to Lightroom Classic.
Cloud Queue
When using Cloud Rendering, the Cloud render queue is used to monitor your image status.
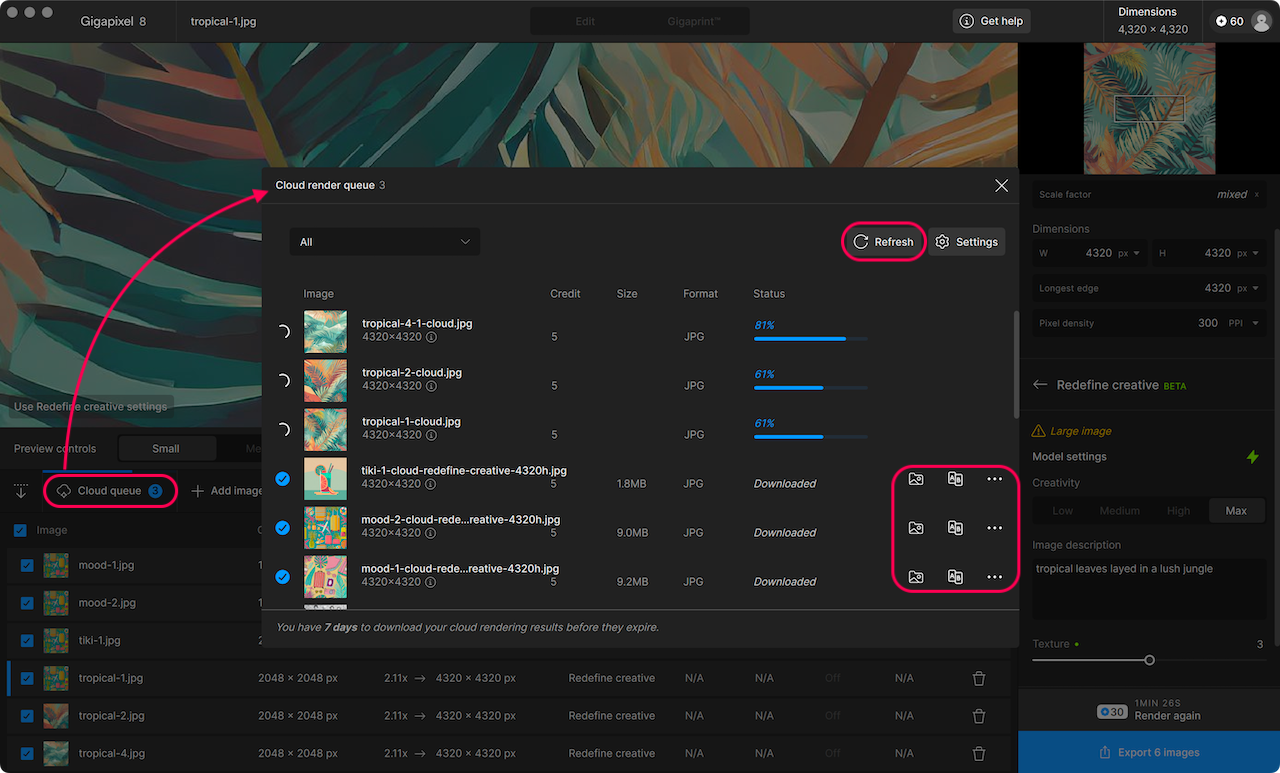
- Use the refresh button if renders appear stuck
- Use the folder icon to navigate to the downloaded image
- Use the A|B button to compare in the cloud
- Use the ••• button to gather the request ID for support
Unexpected Results
False Resolution
If an image source came from scanners, screen captures, or somewhere online; it may have the issue of false resolution. False resolution happens when an image is upsampled, boosting pixel count without adding real detail. The image source may have large dimensions, but the extra pixels are interpolated and don’t reflect true information from the original image. Downscaling removes excess pixels and condenses real detail, restoring clarity by eliminating false resolution.
False resolution can easily be recognized by viewing the original image at 100% or actual size. If you’re seeing blocks of compression artifacts, visible pixel stepping, or artifacts in areas that should otherwise be smooth; it is likely that your image suffers from false resolution and needs to be downscaled before being upscaled in Gigapixel.
Before upscaling, try applying a 1x scale factor to the image using Recover v2 and either Low, Medium, or High pre-downscaling applied.
Very Small Sources
Depending on the dimensions and quality of the source image, there might not be enough information for the AI models to work with, so the results display made-up detail to complete the upscaling task. Since we can imagine what the scene should look like in reality, these AI results appear unnatural. Some images simply aren't good candidates for outstanding results.
Choosing Models
Depending on the contents of the image, some models with a mix of settings will perform better than others. Using the Compare tool is the best way to experiment with possible results. We always recommend starting with Auto mode applied to any image and adjusting from there.
Ensure you're using the right model for the intended use case. For example, Generative models are designed to be used with smaller images, about 1MP in resolution. For larger image sources and modern photography, use the Core models.
If your system suffers from slow performance, using the lesser demanding Legacy models might help.